When you’re navigating any computer setup, understanding the specific details of your hardware components is often quite important.
The graphics card, also commonly referred to as a video card or GPU (Graphics Processing Unit), is one such component that frequently comes into focus, especially when discussing system performance.
In this guide, I’ll walk you through several straightforward methods to retrieve your graphics card information directly on your Ubuntu 24.04 system.
We’ll explore techniques using both the ever-reliable command line and some user-friendly graphical tools. For each method discussed, I’ll provide clear, step-by-step examples, making it simple for you to follow along and find out your Ubuntu GPU model or how to check video card specs Linux systems can report.
Why Is It Useful to Check Your GPU Information?
Gaining a clear understanding of your graphics hardware’s specifications can be incredibly beneficial. This knowledge can assist in diagnosing performance bottlenecks, optimizing games and resource-intensive applications, verifying compatibility between your drivers and operating system, and much more.
We’ll delve into some essential tools that I find quite handy, such as lshw, lspci, HardInfo, and inxi, among others, to extract both fundamental and detailed information about your graphics card in Ubuntu.

Whether you’re a seasoned Linux system administrator or just starting your journey with Ubuntu, these commands are designed to be relatively simple yet powerful. They apply to any Ubuntu desktop or server environment. Let’s begin and explore how to utilize each tool for insightful GPU diagnostics and to easily identify graphics hardware on Ubuntu 24.04.
Read: Troubleshooting Audio Issues (Crackling, No Sound) on Ubuntu 24.04 with PipeWire
Discovering GPU Details with lshw (List Hardware)
A dependable method for displaying graphics card information on Ubuntu involves using the command-line utility lshw, which is short for “list hardware.” This versatile tool is excellent for querying details about various hardware components connected to your system.
Installing lshw on Your Ubuntu System
First, ensure that lshw is installed on your system. If it’s not present, you can easily install it using the apt package manager with the following commands:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install lshw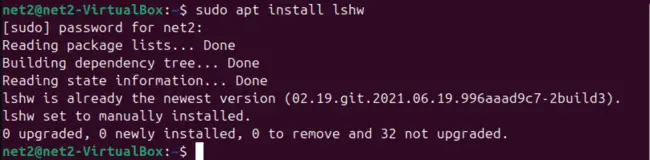
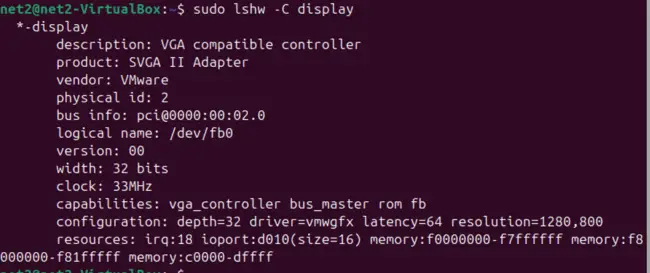
Once lshw is set up, you can specifically request information about display adapters. You’ll likely need to use sudo to get the most comprehensive details:
sudo lshw -C displayChecking Graphics Card Specifics on Ubuntu 24.04 using lshw
Executing this command will provide you with key information about your video card, such as its manufacturer, model name, and occasionally, memory specifications. This is a great way for an Ubuntu find GPU model command line approach.
Utilizing lspci to List PCI Devices
Another excellent command-line tool for checking graphics card information on your Ubuntu machine is lspci. This utility lists all PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect) devices connected to your system, which naturally includes your video card.
Read: How to Fix NVIDIA Installation Conflicts: Disabling the Nouveau Driver on Linux
Running lspci on Linux / Ubuntu 24.04 for GPU Info
To specifically isolate your video card details, you can pipe the output of lspci to the grep command. Most graphics cards are identified as a “VGA compatible controller” or something similar. Give this a try:
lspci | grep -i vga
Alternatively, filtering for “display” might also yield the desired results:
lspci | grep -i display
This command typically provides a concise line showing the manufacturer and model of your GPU, making it a quick Ubuntu check graphics card method.

Employing HardInfo (A Graphical Tool)
If you’re more comfortable with a graphical user interface (GUI), tools are also available for that! A popular choice is HardInfo. It comprehensively overviews your system’s hardware configuration and software environment.
Read: How to Fix WIFI not working on Ubuntu 22.04
Installing the HardInfo Utility on Ubuntu
You can install HardInfo using Ubuntu’s package manager with these commands:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install hardinfo
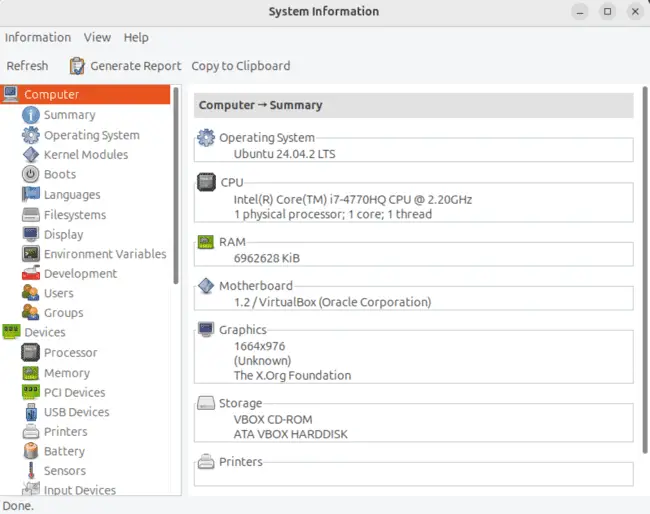
Locating Ubuntu GPU Information with HardInfo
Once installed, launch HardInfo. You might find it listed as “System Profiler and Benchmark” in your applications menu. Within the application window, navigate through the categories listed on the left-hand side. Look under “Devices” → “PCI Devices,” or there might be a dedicated “Display” section. There, you should find detailed information about your Ubuntu video driver and associated hardware.
Using Neofetch for a Stylish System Overview
Neofetch is a nifty command-line tool that presents system information in a visually appealing format, often alongside an ASCII logo of your Linux distribution. Importantly for us, it includes details about your graphics card too!
Installing neofetch on Ubuntu 24.04
To get neofetch up and running, use the following commands:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install neofetch
Displaying Ubuntu Graphics Card Data with neofetch
Simply execute the command neofetch in your terminal. In the output, look for the line labeled “GPU.” This typically shows the model name of your graphics card.
neofetch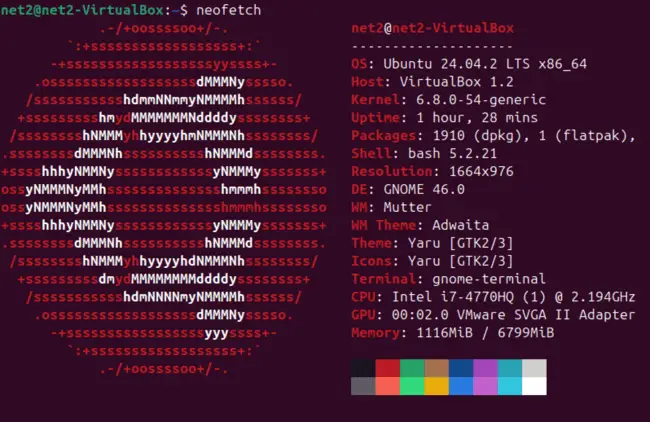
Using Screenfetch (A Neofetch Alternative)
ScreenFetch is another command-line utility, quite similar in function to Neofetch. It generates a text-based summary of your system specifications, including OS version, kernel details, hardware (like CPU, RAM, and, of course, your GPU), and often an ASCII art logo.
Installing screenfetch on Ubuntu 24.04
You can install ScreenFetch with this simple command sequence:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install screenfetch
Read: How to fix Bluetooth connection issues on Ubuntu 22.04
Just like with Neofetch, simply run the command to view the output:
screenfetch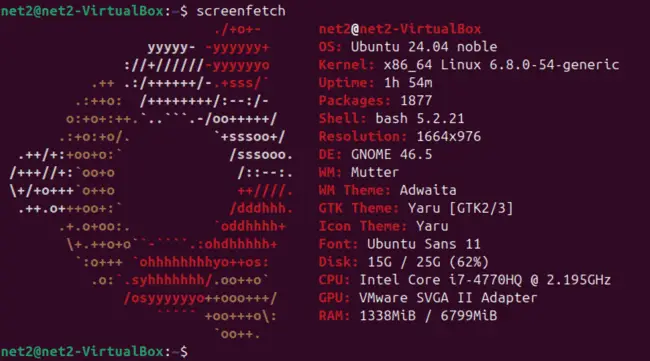
Ubuntu check graphics card using screenfetch
Read: How to Install an SMTP Server on Ubuntu 22.04
Leveraging inxi for In-Depth Hardware Information
inxi is a powerful and comprehensive command-line script that provides extensive system hardware information. It’s particularly adept at delivering detailed graphics card specifications, making it a go-to for an “Ubuntu identify GPU” task.
Installing inxi on Ubuntu 24.04
Install inxi using the apt package manager:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install inxi
To obtain detailed graphics information, use the -G flag. Appending an x (e.g., -Gx) will provide even more extensive details:
inxi -Gx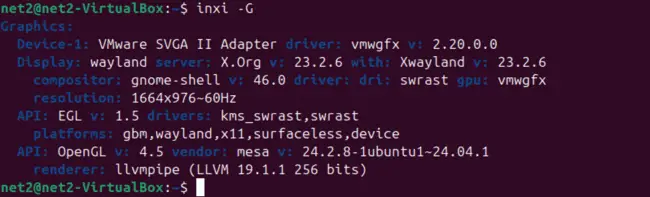
inxi offers many useful options for querying system hardware. Here are a few common ones:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
inxi -F | Shows full system information (CPU, RAM, GPU, OS, etc.). |
inxi -b | Displays basic output, which includes GPU information. |
inxi -G | Focuses specifically on graphics card details (like how to check graphics card details on Ubuntu 24.04). |
inxi -S | Shows system host information. |
inxi -C | Shows CPU information. |
inxi -M | Shows motherboard information. |
Exploring OpenGL Details with glxinfo
glxinfo is a command-line tool specifically crafted to display information about the OpenGL implementation on your Linux system. This is particularly useful for checking details such as the supported OpenGL version, the graphics driver vendor, and specifics about the graphics card’s capabilities concerning OpenGL. It’s often consulted when troubleshooting graphics-related issues, especially with games or applications that rely on OpenGL.
To use glxinfo, you’ll first need to install the mesa-utils package. You can achieve this with the following command:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install mesa-utils
Once installed, you can run glxinfo. Using the -B flag provides a concise summary, which is often exactly what you need:
glxinfo -B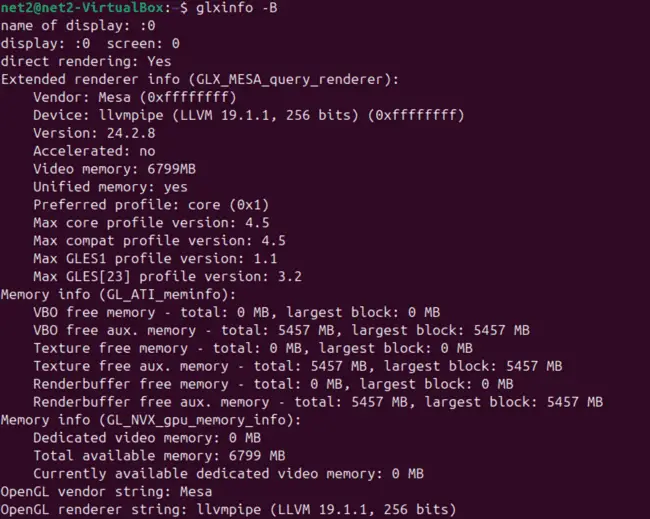
glxinfo Ubuntu command output example
Read: Top Break Reminder Applications for Ubuntu to Boost Well-being
Managing Display Configurations with xrandr
xrandr (X Resize and Rotate) is a standard command-line utility used to manage screen resolutions, refresh rates, and multi-monitor setups within Xorg sessions. While its primary function is configuration, it can also provide some basic information about connected displays and the graphics adapter that powers them.
The good news is that xrandr typically comes pre-installed with the standard graphical environment on Ubuntu, so you usually don’t need to install anything extra.
To see the connected monitors and their current settings, you can run:
xrandr
For a simpler list of connected monitors, you can use:
xrandr --listmonitors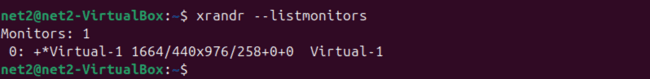
While xrandr doesn’t provide detailed GPU model information, it helps confirm which display outputs are active and their resolutions, which is directly related to the graphics card’s function.
Using nvidia-smi for NVIDIA GPUs
If your system is equipped with an NVIDIA graphics card and you have installed the official NVIDIA drivers, the nvidia-smi (NVIDIA System Management Interface) command is an invaluable tool. It provides highly detailed information about the GPU’s current state, usage metrics, temperature, memory utilization, processes utilizing the GPU, and the installed driver version. This is key for getting NVIDIA GPU info on Ubuntu.
Simply run it in your terminal (it’s usually installed automatically with the NVIDIA driver):
nvidia-smi
This is widely considered the go-to utility for monitoring and querying NVIDIA GPUs on Linux systems.
A Note on fglrxinfo (for Older AMD GPUs)
For older AMD/ATI graphics cards that utilized the legacy proprietary fglrx driver (which is generally not recommended or available on modern Ubuntu versions like 24.04), the fglrxinfo command was the tool used to display GPU and driver information.
If you were, for some reason, using this older driver on a compatible system, you would run:
fglrxinfo
It’s important to remember that modern AMD GPUs on Ubuntu 24.04 typically use the open-source amdgpu kernel driver. For these, tools like lspci, lshw, inxi, and glxinfo are far more relevant for getting AMD GPU details on Ubuntu.
Checking Vulkan Support with vulkaninfo
If your graphics card and its driver support the Vulkan graphics API (which is common for modern gaming and demanding applications), the vulkaninfo tool can provide extremely detailed information. This includes Vulkan capabilities, device properties, supported extensions, and available layers.
You might need to install it first if it’s not already on your system:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install vulkan-tools
Then, execute the command:
vulkaninfo
The output from vulkaninfo is typically very verbose but contains an exhaustive list of details regarding Vulkan support on your GPU.
Understanding Driver Management with gpu-manager
Ubuntu includes a utility called ubuntu-drivers (with related functionalities sometimes accessed via commands that interact with gpu-manager). This tool primarily helps manage graphics drivers, especially for switching between open-source and proprietary drivers (like those from NVIDIA). While not its main purpose to display hardware specs, checking its status can sometimes offer clues about the current driver configuration.
You can list recommended drivers using:
ubuntu-drivers devices
Running gpu-manager directly might provide logs or status information, which is often particularly relevant for NVIDIA Optimus setups (laptops featuring both integrated and dedicated GPUs). Its output isn’t standardized for a general specification display but can be useful for driver troubleshooting scenarios.
gpu-managerFinal Thoughts and Key Takeaways
And there you have it – a comprehensive look at several effective methods to display graphics card information on your Ubuntu 24.04 system! We’ve explored command-line mainstays like lspci, lshw, and the very detailed inxi, as well as graphical alternatives such as HardInfo and specialized utilities like nvidia-smi for NVIDIA cards or glxinfo for OpenGL details.
Utilizing these tools makes it straightforward to gather crucial details about your GPU, including its manufacturer, model, sometimes memory size, and the current driver version it’s operating with. This information proves incredibly valuable when you’re troubleshooting graphics-related glitches, aiming to optimize settings for games or graphics-intensive applications, or simply verifying hardware compatibility.
One final piece of advice from my experience: always remember that keeping your graphics drivers up-to-date is generally a good practice for achieving the best possible performance and system stability. New driver releases often come packed with important bug fixes and performance enhancements that can significantly improve your user experience.
If you like the content, we would appreciate your support by buying us a coffee. Thank you so much for your visit and support.