As a Linux user, particularly on Ubuntu (though this is relevant for most major distributions), you might have experienced your system becoming slower over time.
This can happen even with powerful computer hardware. If you’re looking for an Ubuntu performance optimization guide, you’ve come to the right place. If your Linux system feels sluggish, or tasks are taking longer than expected, there are several potential reasons. Fortunately, there are also many solutions to boost performance and improve Linux system efficiency.
Some tasks and services may take a long time to execute, despite your processor being capable of handling many operations easily. The reasons vary, but the most frequent ones are:
- Too many applications are open, consuming your RAM.
- Unnecessary applications start automatically at boot, using up resources. This is why it’s crucial to optimize Ubuntu startup services.
- Your hardware may not be able to handle the increasing demands efficiently (older specifications, e.g., hard disk, CPU).
This article will guide you on pinpointing the causes of your system’s slow performance (including swap memory, RAM, CPU, hard disk health, and startup services). We will explore common techniques to speed up Ubuntu 24.04 performance by optimizing hardware, software, and configuration.
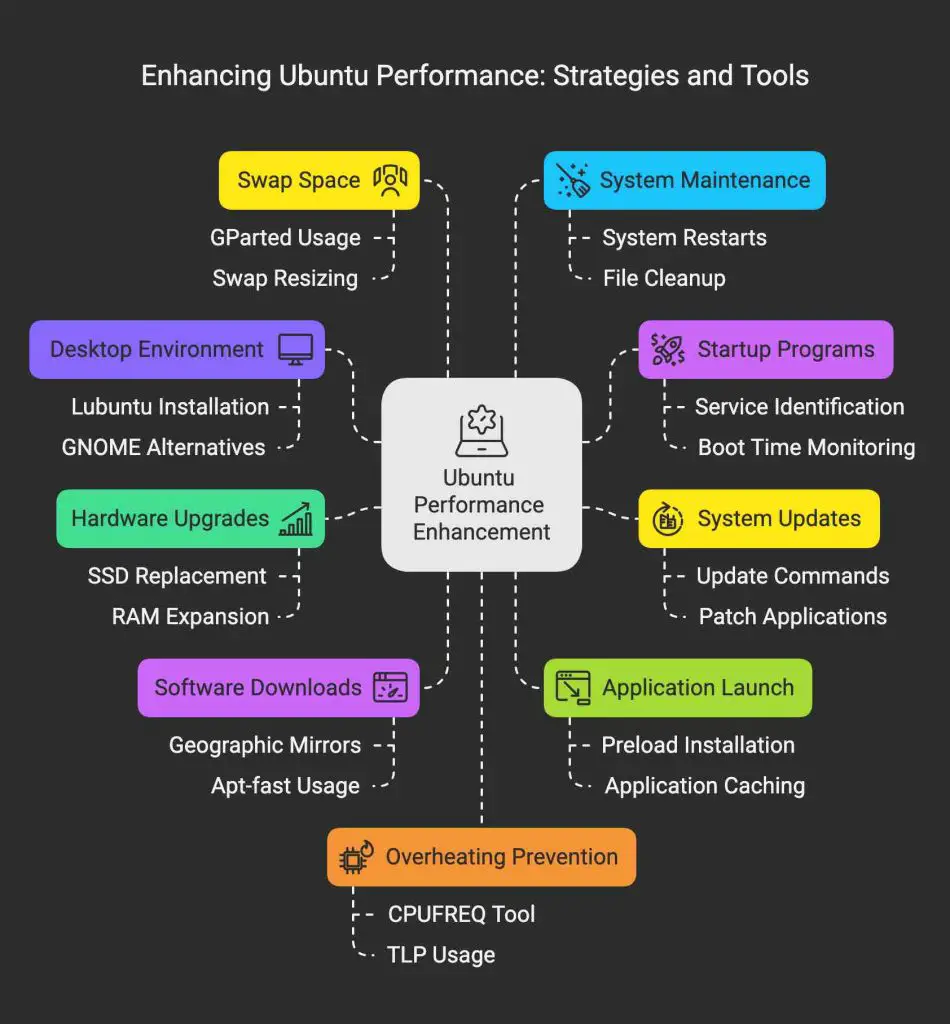
The mind map illustrates our comprehensive approach to enhancing Ubuntu’s performance. It captures the key optimization areas we’ll explore throughout this article—from hardware upgrades and swap management to desktop environment customization and startup optimization. As we proceed, we’ll examine each branch in detail, providing practical techniques to significantly improve your system’s responsiveness and efficiency. By the end of this article, you will be equipped to troubleshoot and enhance your Linux system’s speed.
Read: Best Partition Managers for Linux Users
Choose a Faster Desktop Environment
To enhance your system’s performance, consider installing the GNOME 3 desktop. It’s designed for efficient resource usage and smooth graphics, but it needs robust hardware. If you have an older computer, you might find it slow. A good solution is Lubuntu, a lightweight version of Ubuntu that uses an LX-based desktop environment. Install it using this terminal command:
sudo apt-get install lubuntu-desktop
Alternatively, you can select an Ubuntu version that includes Lubuntu by default. Also, think about using lighter alternatives for common applications. For instance, use GDebi for installing packages, AbiWord instead of LibreOffice Writer, or AppGrid instead of the Ubuntu Software Center. This contributes to overall Ubuntu performance optimization.
Manage Startup Programs and Services
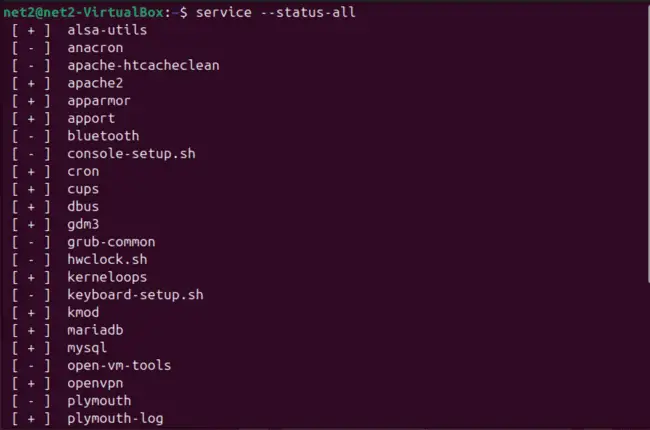
To see a list of services that launch when your computer starts, open your terminal and execute this command:
service --status-all
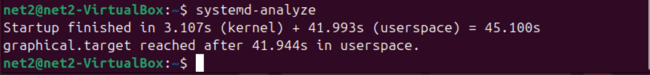
If your system uses systemd (a comprehensive system and service manager), you can check the boot-up time with this command:
systemd-analyze
This shows how long the kernel, userspace, and initrd took to start during boot. This is a key step to improve Linux system efficiency.
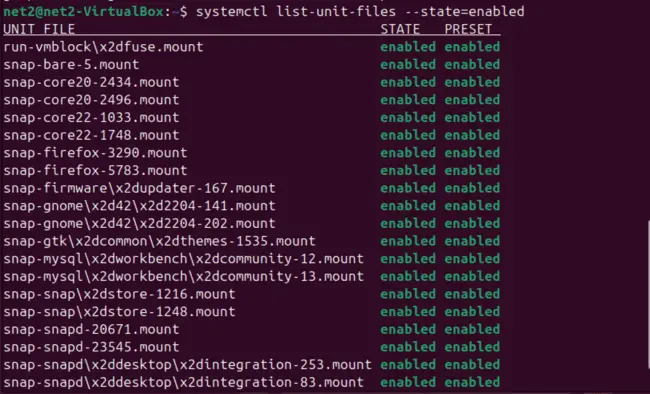
To list enabled services (those that start automatically) using systemd’s systemctl, use:
systemctl list-unit-files --state=enabled
To see a list of running services, sorted by how long they took to initialize, use the blame option with systemd-analyze:
systemd-analyze blame
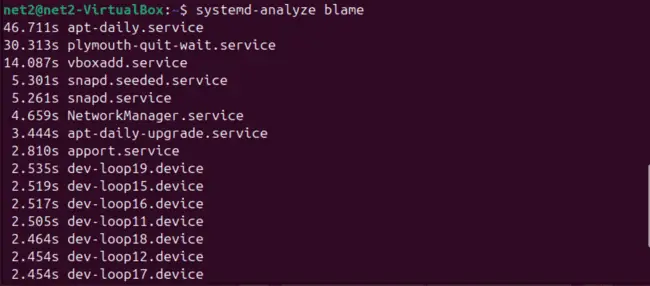
Use the Enter key to scroll through the list, and press ‘q’ to exit.
This helps you identify services that took an unusually long time to start. Effectively, this lets you optimize Ubuntu startup services. To prevent a service from running at boot, use:
sudo systemctl disable service_name
On Ubuntu 24.04, you can also use a graphical application called “Startup Applications” to manage programs that launch at startup. Find it in the Activities menu.

When the window appears:
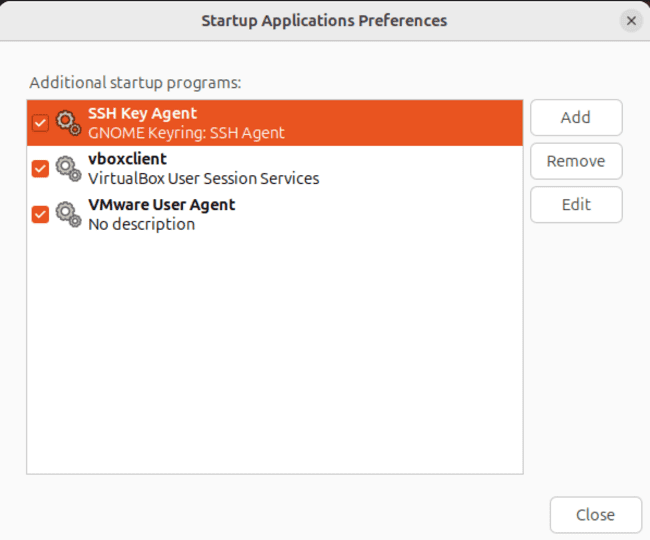
Select the application you want to manage, and click “Remove” to stop it from starting automatically.
Read :How to install and uninstall applications on Ubuntu ?
Install Ubuntu Updates Regularly
Ubuntu releases updates to address known problems and enhance the system’s overall performance and efficiency. Regular updates are a cornerstone of any Ubuntu performance optimization guide. It’s crucial to understand the Ubuntu release cycle to know which version you can upgrade to. Canonical releases a Long Term Support (LTS) version every two years in April, which is used by the vast majority of Ubuntu installations. Interim releases are published every six months, providing users with newer features for improved stability, usability, and performance.
To get the latest updates, open the terminal and run: sudo apt-get update. If your release is outdated, check for a major upgrade by running: sudo apt-get upgrade and press “Y” when prompted. Remember to back up your files before upgrading.
Upgrade to an SSD for Faster Storage
Solid State Drives (SSDs) offer significantly faster read and write speeds compared to traditional mechanical hard drives. This is one of the most impactful ways to speed up Ubuntu 24.04 performance. Be sure to purchase the correct model for your specific computer.

Add More RAM for Improved Performance
Ubuntu 24.04 requires at least 2GB of RAM for smooth operation. Increasing your RAM can significantly improve your computer’s overall speed, especially if you use resource-intensive applications like video editors or games. This is a direct way to improve Linux system efficiency.
Read: How to encrypt a USB stick on Ubuntu
You can manually install new RAM modules. Ensure you get the correct type that is compatible with your computer’s RAM slots.
To check how much RAM your system currently has, use this terminal command:
free –m
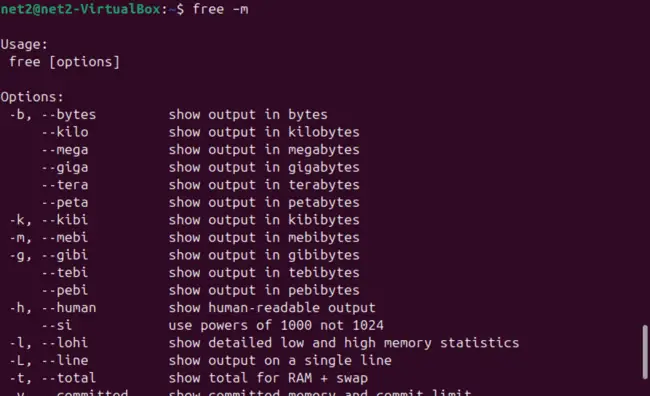
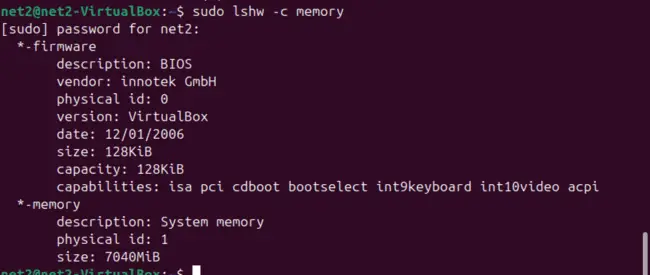
To see your Ubuntu RAM type and other details, run:
sudo lshw -c memory
Read: How to fix high memory usage in Ubuntu
Select a Nearby Software Download Mirror
Using a software update mirror that’s geographically close to you can significantly speed up downloads. This simple step can surprisingly improve Linux system efficiency during updates. Ubuntu software repositories are mirrored (copied) in many countries. While this is usually selected automatically during setup, it’s good to verify you’re using the nearest mirror.
To adjust mirror settings, go to Activities and type “Software”.
Select the option labeled “Software Updater,” as shown above. A new window will open.
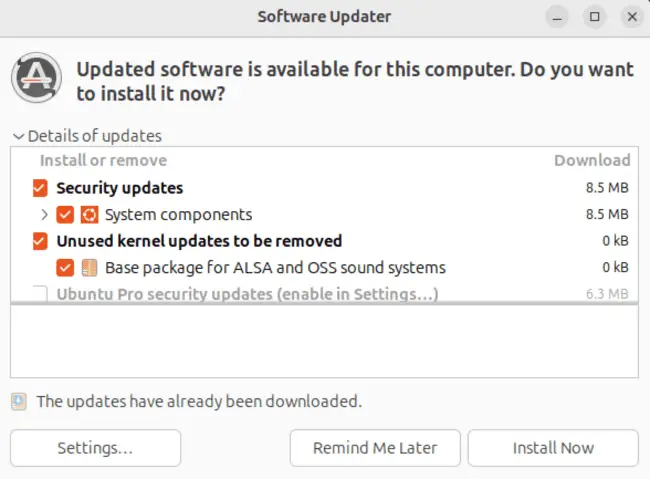
Click the “Settings” button. This will bring up another dialog box.
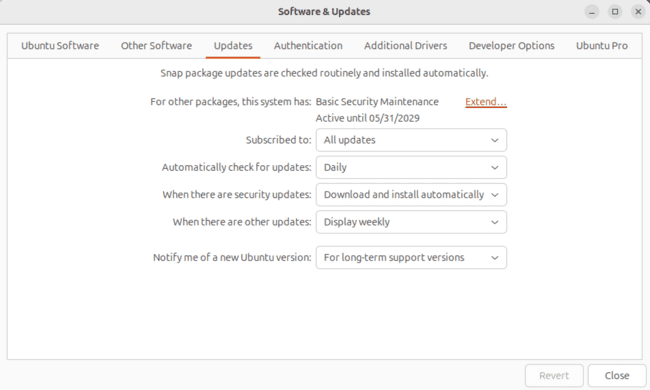
To choose the server closest to your location, click the dropdown menu next to “Download from”. Alternatively use the shell script “apt-fast”, that can be used as wrapper for “apt-get”, to automatically download packages from various locations. To try using that tool, install it from the official PPA by running these commands:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:apt-fast/stable sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install apt-fast
Read: What you need to do to secure Ubuntu
Use Preload to Speed Up Application Launch
To improve application loading times, you can use Preload, a daemon that runs in the background. It analyzes how you use software and caches frequently used applications, making them launch faster. This is a passive way to speed up Ubuntu 24.04 performance.
To install Preload on Ubuntu, open a terminal and run:
sudo apt-get install preload
After installation, restart your computer. Preload will run in the background, and you should notice that your frequently used applications open more quickly.
Adjust Swap Space if Needed
Swap space can help speed up your system if your Linux machine doesn’t have enough RAM to handle its workload. Proper swap configuration is part of a complete Ubuntu performance optimization guide.
When you install Ubuntu, a dedicated swap partition is usually created on your hard drive. Over time, you might need to increase the swap size. You can do this using GParted, Ubuntu’s default disk management tool.
Read: How to fix : Unable to install GParted on Ubuntu
In your Activities, type “GParted” and open it. If does not show up, you would need to install it using the command :
sudo apt install gparted
Now you can invoke gparted by typing: gparted in the terminal. It will bring up the window shown below :
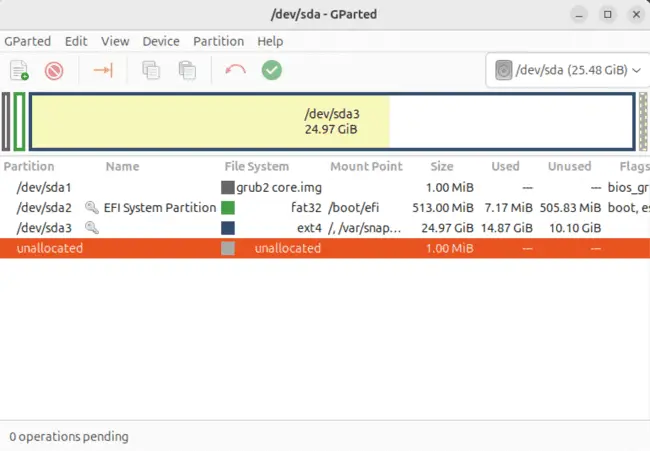
You can, for example, shrink your main partition after deleting the existing swap partition.
Read: How to increase swap space in Linux
After that, create a new partition to allocate more space to swap. Refer to the GParted help manual if needed. Be very careful when resizing partitions, as it’s a sensitive operation. Always back up your data beforehand.
Restart Your Computer Regularly
As you use your computer, open applications, running processes, and services accumulate, both in the foreground and background. This can slow down your system because resources like RAM, swap, and CPU are being used. A simple solution is to shut down your computer at least once or twice a week. Simply putting it to sleep doesn’t solve the problem, as the processes remain active. This simple habit can significantly improve Linux system efficiency.
Read: How to Troubleshoot and Optimize Ubuntu Startup: Manage Systemd Services for Faster Boot Time
Remove Unnecessary Files and Applications
Over time, unnecessary files can build up on your system. This can impact Ubuntu’s performance, especially if you don’t have an SSD. Uninstall applications you no longer use and remove unnecessary files (check your Downloads folder, for example). Keeping your system clean is essential for long-term Ubuntu performance optimization.
To clear the temporary cache used by `apt-get`, run:
sudo apt-get clean
You can also safely remove unused packages and dependencies with:
sudo apt-get autoremove
Read: how to keep your Ubuntu clean
Prevent Overheating to Maintain Performance
You might have noticed that a hot computer runs slowly. Overheating can negatively affect overall system performance. Two tools, CPUFREQ and TLP, can help mitigate this. Managing temperature is a key, and often overlooked, aspect of how to speed up Ubuntu 24.04 performance.
The CPUFREQ indicator lets you adjust CPU algorithms, allowing the processor to change its frequency based on temperature and power consumption. Install it with:
sudo apt-get install indicator-cpufreq
After restarting, consider using the “Powersave” mode.
To install TLP, run these commands:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:linrunner/tlp sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install tlp tlp-rdw
To start TLP, use:
sudo tlp start
TLP will then run as a background process.
Read: How to save power on Linux Ubuntu/Debian using cpufreq
Monitor CPU Usage to Find Bottlenecks
As mentioned earlier, a hot CPU might be caused by intensive computations from background applications, some of which may be unnecessary. A key part of any Ubuntu performance optimization guide is knowing how to monitor your system. To check the current CPU load, use the top command, a Linux system monitor. It offers insights into a Linux server’s performance and health.
IT administrators rely on system monitors, like top, to track key metrics, including CPU usage, memory consumption, and running processes, in real time. Understanding top‘s output helps identify resource bottlenecks, troubleshoot problems, and optimize performance. It’s an essential skill for Linux server administrators. top provides granular visibility into server operations with robust filtering and customization options.
The top utility allows you to sort processes by CPU usage. Run it with:
top
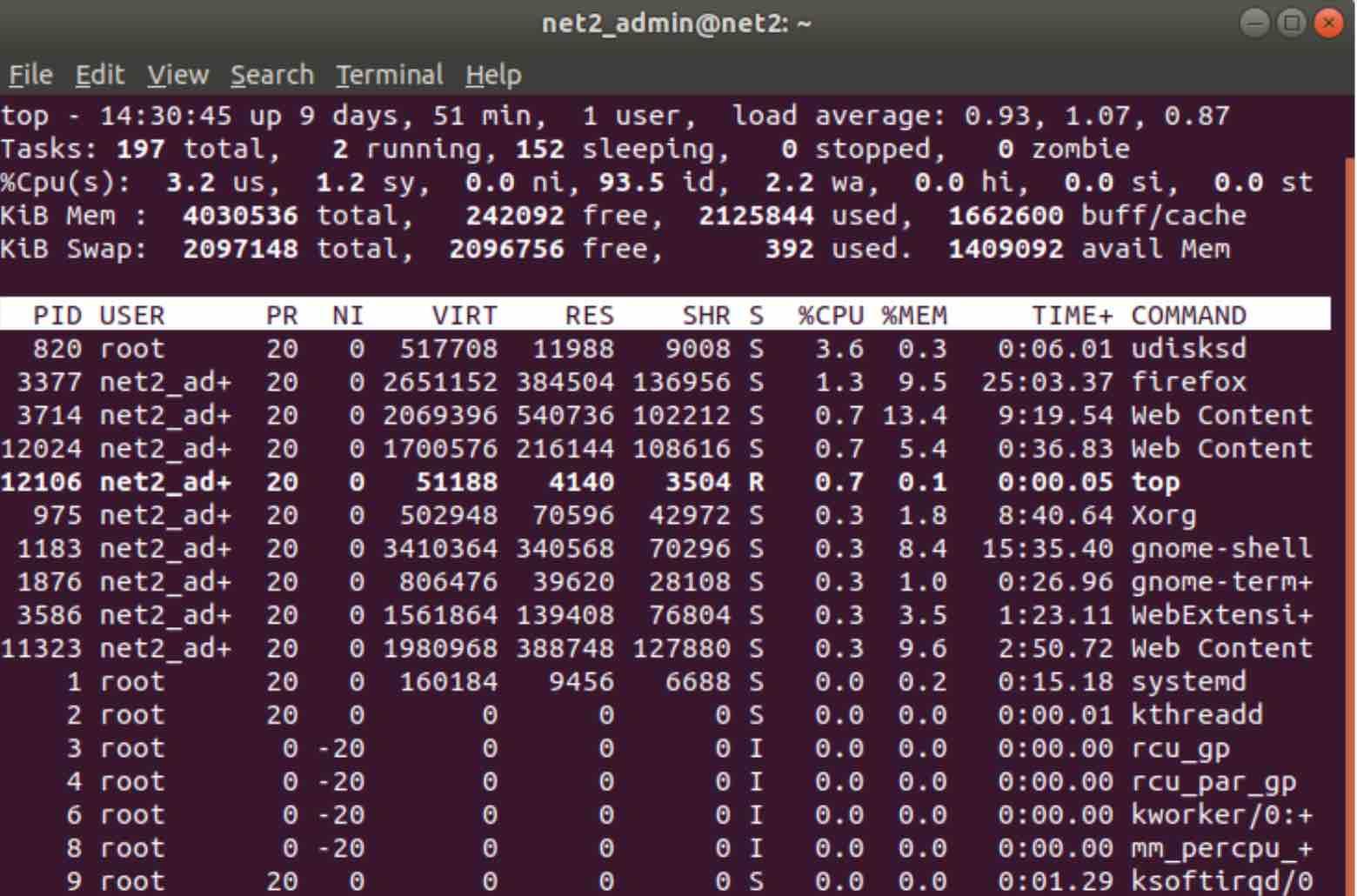
The screenshot shows processes that are straining the CPU. You can terminate them using the kill command.
Read: Top 41 Essential Linux Performance Monitoring Tools for System Administrators
Check Disk I/O Activity
To monitor your Linux Disk I/O (Input/Output) usage, you can use iotop, a free utility similar to top. It displays a table of I/O usage by processes or threads. Install it with:
sudo apt install iotop
After installation, start iotop with:
sudo iotop
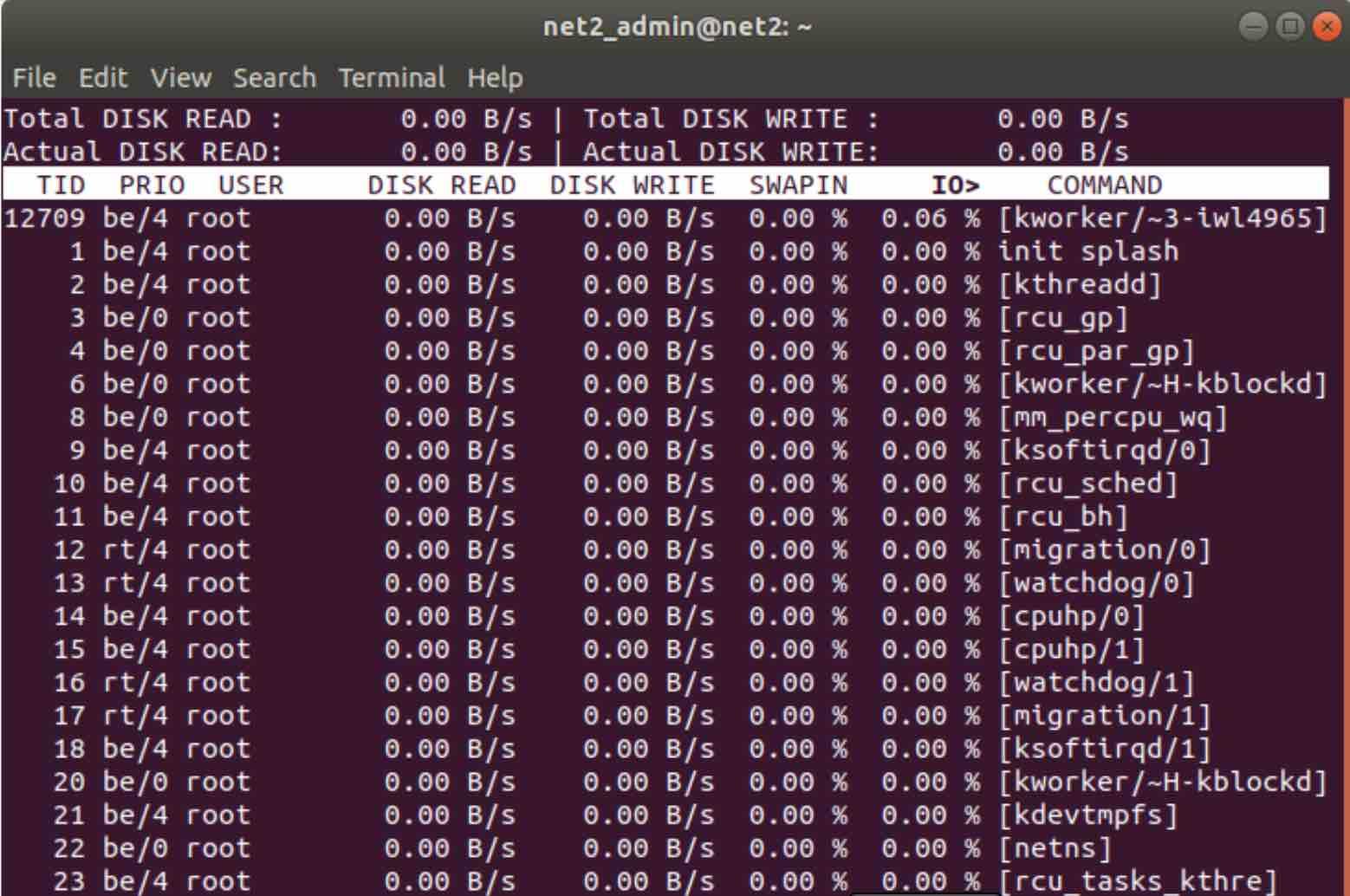
In the screenshot above, the system is idle, as indicated by zeros across the screen. You might occasionally see small, positive values, representing data being read or written, as shown below for the systemd-journald process:
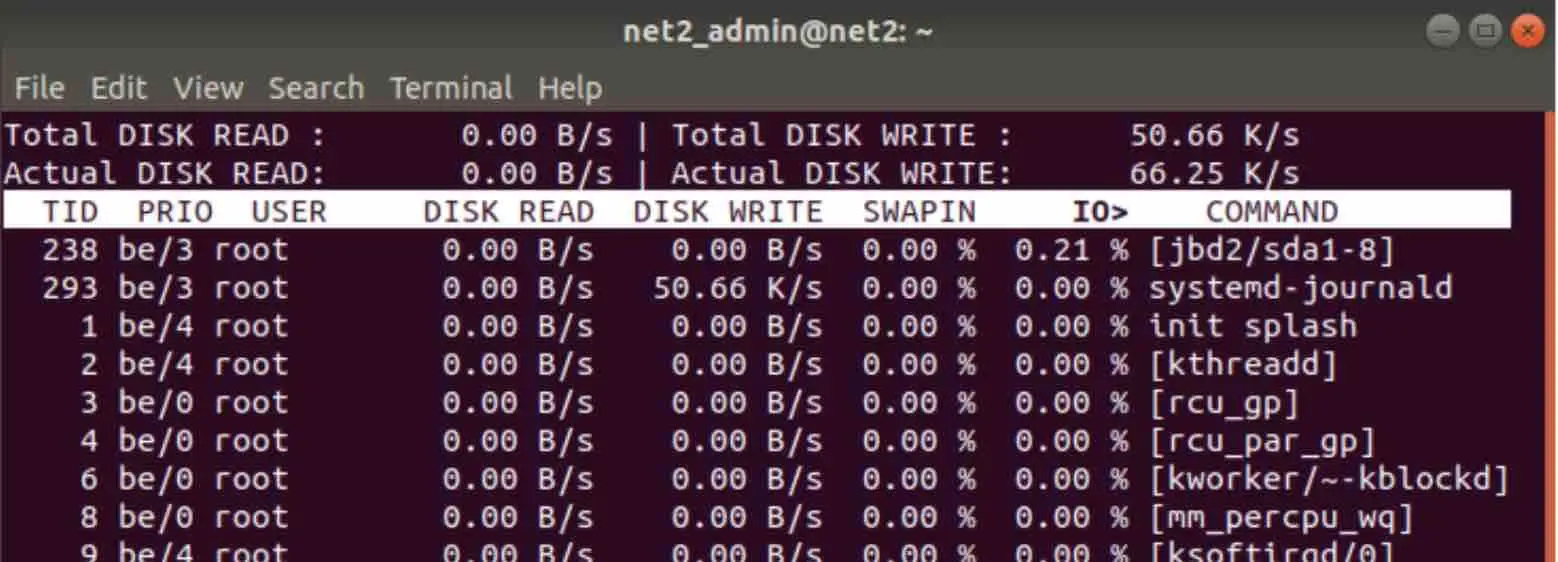
You can now identify processes that are consuming a lot of I/O resources and take appropriate action. This helps to finely tune and improve Linux system efficiency.
Read: What to do when Ubuntu freezes
Conclusion
A common reason for a slow Linux system is having too many open applications or running processes, which consume resources like RAM and CPU. Another issue is not shutting down the system regularly, leading to a buildup of unnecessary background processes. To address these, close unused applications and shut down your system regularly. Additionally, using Linux performance monitoring tools can help you diagnose and resolve system slowdowns effectively. By following this Ubuntu performance optimization guide, you should be able to significantly speed up Ubuntu 24.04 performance and enjoy a more responsive system.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
I. General Performance and Troubleshooting:
- Q: Why is my Ubuntu 24.04 system running slow even with good hardware?
- A: Slowdowns can occur due to multiple open applications consuming RAM, unnecessary startup programs, or hardware limitations (like a traditional hard drive). The article addresses all these issues.
- Q: How can I identify the cause of slow performance on my Ubuntu system?
- A: The article recommends monitoring RAM, CPU, swap space, disk I/O, and startup services to pinpoint bottlenecks. Tools like
top,iotop,free, andsystemd-analyzeare discussed.
- A: The article recommends monitoring RAM, CPU, swap space, disk I/O, and startup services to pinpoint bottlenecks. Tools like
- Q: What are the most common reasons for a slow Ubuntu system?
- A: The most frequent causes are: too many applications running, unnecessary startup programs, and hardware limitations (especially using an HDD instead of an SSD).
- Q: How can I improve the overall efficiency of my Linux system?
- A: By applying the techniques provided by the article such as : Choosing a Faster Desktop Environment, Managing Startup Programs and Services and Installing Ubuntu Updates Regularly.
II. Desktop Environment and Application Choices:
- Q: How can I make Ubuntu faster by choosing a lighter desktop environment?
- A: The article recommends Lubuntu (with its LX-based desktop) as a lightweight alternative to the default GNOME 3, especially for older hardware. Install it with:
sudo apt-get install lubuntu-desktop
- A: The article recommends Lubuntu (with its LX-based desktop) as a lightweight alternative to the default GNOME 3, especially for older hardware. Install it with:
- Q: What are some lightweight application alternatives to improve Ubuntu performance?
- A: The article suggests GDebi (for package installation), AbiWord (instead of LibreOffice Writer), and AppGrid (instead of the Ubuntu Software Center) as lighter alternatives.
III. Managing Startup Programs and Services:
- Q: How can I see a list of all services that start automatically on my Ubuntu system?
- A: For systems using
systemd:systemctl list-unit-files --state=enabled - For older systems (or to see all services, including non-systemd ones):
service --status-all
- A: For systems using
- Q: How do I check how long my Ubuntu system takes to boot and which services are slowing it down?
- A: Use
systemd-analyzeto see total boot time. Usesystemd-analyze blameto see a list of services sorted by their initialization time.
- A: Use
- Q: How can I prevent a specific service from starting automatically on boot in Ubuntu?
- A: Use:
sudo systemctl disable service_name(replaceservice_namewith the actual service name).
- A: Use:
- Q: How can I manage startup applications graphically in Ubuntu 24.04?
- A: Use the “Startup Applications” utility (found in the Activities menu). You can add, remove, or edit startup programs there.
IV. System Updates and Software Sources:
- Q: Why is it important to install Ubuntu updates regularly for performance?
- A: Updates often include performance improvements, bug fixes, and security patches that can make your system run smoother and more efficiently.
- Q: How do I update my Ubuntu system from the terminal?
- A: Use:
sudo apt-get update(to update package lists) andsudo apt-get upgrade(to install updates).
- A: Use:
- Q: How can I speed up software downloads on Ubuntu by choosing a closer mirror?
- A: Go to “Software & Updates” (search for it in Activities), click the “Settings” button, and then choose a server from the “Download from” dropdown that’s geographically close to you.
- Q: What is
apt-fast, and how can it help speed up software installation on Ubuntu?A: `apt-fast` is a wrapper for `apt-get` that downloads packages from multiple mirrors simultaneously,potentially speeding up the download process. Install it with:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:apt-fast/stable
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install apt-fast
V. Hardware Upgrades (SSD and RAM):
- Q: What is the most impactful hardware upgrade to speed up my Ubuntu system?
- A: Upgrading from a traditional hard drive (HDD) to a solid-state drive (SSD) will provide a significant performance boost.
- Q: How much RAM does Ubuntu 24.04 need for smooth operation?
- A: At least 2GB is recommended, but more RAM (4GB, 8GB, or more) will significantly improve performance, especially if you use resource-intensive applications.
- Q: How can I check how much RAM my Ubuntu system currently has?
- A: Use the command:
free -m(the output is in megabytes).
- A: Use the command:
- Q: How can I find out the type of RAM my Ubuntu system uses?
- A: Use the command:
sudo lshw -c memory
- A: Use the command:
VI. Preload and Application Launch Speed:
- Q: How can I make applications launch faster on Ubuntu using Preload?
- A: Install Preload:
sudo apt-get install preload. It runs in the background, analyzes your application usage, and caches frequently used applications, making them load faster.
- A: Install Preload:
VII. Swap Space Management:
- Q: What is swap space, and how can it help with Ubuntu performance?
- A: Swap space is a portion of your hard drive (or SSD) used as virtual RAM when your physical RAM is full. It can prevent crashes and improve performance when you’re running out of RAM.
- Q: How can I increase the size of my swap space on Ubuntu?
- A: The article recommends using GParted (a graphical partition editor). Be very careful when resizing partitions, as data loss is possible. Back up your data first. Install GParted with
sudo apt install gparted, then launch it and carefully adjust your partitions.
- A: The article recommends using GParted (a graphical partition editor). Be very careful when resizing partitions, as data loss is possible. Back up your data first. Install GParted with
VIII. System Maintenance and Cleanup:
- Q: Why is it important to restart my Ubuntu computer regularly?
- A: Restarting clears out accumulated processes and services running in the background, freeing up resources (RAM, CPU, swap) and improving performance. Simply putting your computer to sleep doesn’t have the same effect.
- Q: What command is used to invoke gparted?
- A:
gparted
- A:
- Q: How can I remove unnecessary files and applications to improve Ubuntu performance?
- A: Uninstall applications you no longer use. Clean out your Downloads folder and other locations where temporary files might accumulate.
- Q: How can I clean the
apt-getcache on Ubuntu?- A: Use:
sudo apt-get clean
- A: Use:
- Q: How can I remove unused packages and dependencies on Ubuntu?
- A: Use:
sudo apt-get autoremove
- A: Use:
IX. Overheating Prevention:
- Q: How can overheating affect my Ubuntu system’s performance?
- A: A hot computer, especially the CPU, will often slow down to prevent damage.
- Q: What tools can I use to manage CPU frequency and prevent overheating on Ubuntu?
- A: The article recommends
indicator-cpufreq(install withsudo apt-get install indicator-cpufreq) and TLP. Install TLP with:sudo add-apt-repository ppa:linrunner/tlp sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install tlp tlp-rdw sudo tlp start
- A: The article recommends
X. System Monitoring (CPU and Disk I/O):
- Q: How can I monitor CPU usage on Ubuntu to identify processes that are slowing down my system?
- A: Use the
topcommand. It shows a real-time, sorted list of processes, with the most CPU-intensive ones at the top.
- A: Use the
- Q: How can I monitor disk I/O activity on Ubuntu to find processes that are reading/writing excessively?
- A: Use the
iotopcommand (install withsudo apt install iotop). It shows a real-time view of disk I/O usage by different processes.
- A: Use the
- Q: what does the
topcommand do ?- A: The
toputility allows you to sort processes by CPU usage.
- A: The
If you like the content, we would appreciate your support by buying us a coffee. Thank you so much for your visit and support.



