If you are using Ubuntu 22.04 (or prior versions), you might encounter some issues that prevent your system from working properly. For example, you might have a corrupted file system, a broken package, a misconfigured driver, or a forgotten password. In such cases, you can use the recovery mode feature in Ubuntu to diagnose and fix the problems.
Recovery mode is a special boot option that gives you access to various tools and commands that can help you repair your system. You can use recovery mode to clean up disk space, update packages, check file system errors, update the boot loader, enable networking, and more.
In this article, we will show you how to boot Ubuntu into recovery mode and use the different options available. We will also explain what each option does and when to use it.
Read: How to restore GRUB Bootloader in Ubuntu
How to Boot Ubuntu into Recovery Mode
To boot Ubuntu into recovery mode, you need to access the GRUB boot menu first. GRUB is the program that loads Ubuntu and other operating systems on your computer. To access the GRUB menu, you need to restart your computer and press the F12 key. You can also use the following command in the terminal to reboot your computer:
sudo reboot
How to allow the Ubuntu GRUB menu at Boot
Another possibility would be to access the Grub file as follows:
sudo nano /etc/default/grub
This will open up the GRUB file as shown below :
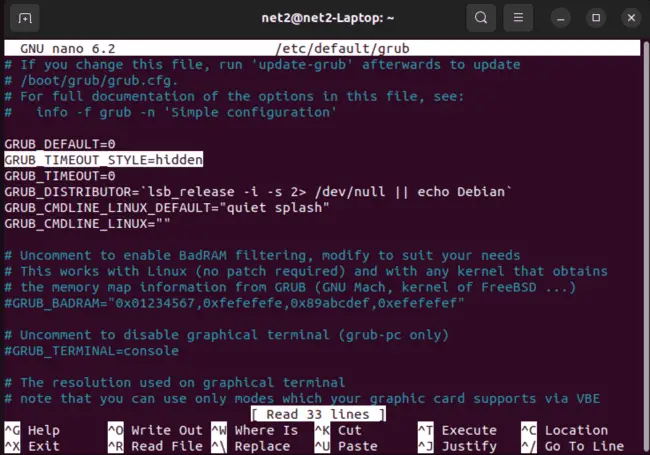
Read: How to fix Ubuntu boot issues
Now change the selected line:
GRUB_TIMEOUT_STYLE=hidden
This line tells GRUB to hide the menu by default. Change it to :
GRUB_TIMEOUT_STYLE = menu
This will make GRUB show the menu every time you boot your system. You can also adjust the value of GRUB_TIMEOUT, which is the number of seconds that GRUB waits before automatically selecting the default entry. For example, if you want GRUB to wait for 10 seconds, you can change it to :
GRUB_TIMEOUT=5
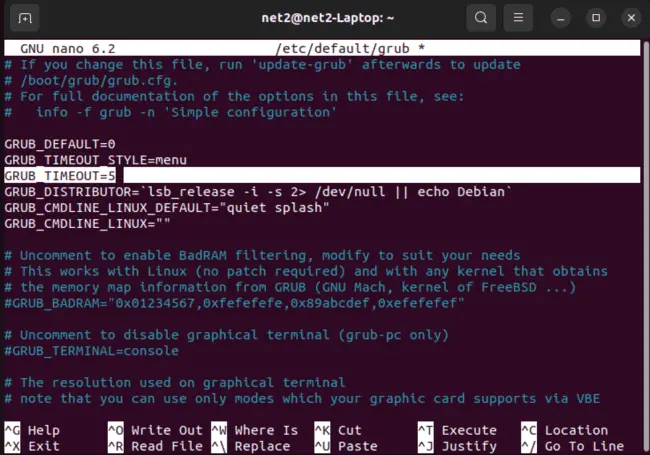
Once you are done, save the file and exit the nano editor.
Now to activate the changes, invoke the command below :
sudo update-grub
You will see some messages on the terminal as GRUB updates its configuration. When your computer restarts, it will show you the GRUB menu. You should see something like this:
Read: How to list, start and stop services at boot time in Linux Ubuntu/Debian
From the GRUB menu, use the arrow keys to select Advanced options for Ubuntu and press Enter.
You will see a sub-menu with different kernel versions. Choose the one that has (recovery mode) at the end and press Enter.
Your computer will boot into Ubuntu recovery mode and show you a menu with several options. You should see something like this:
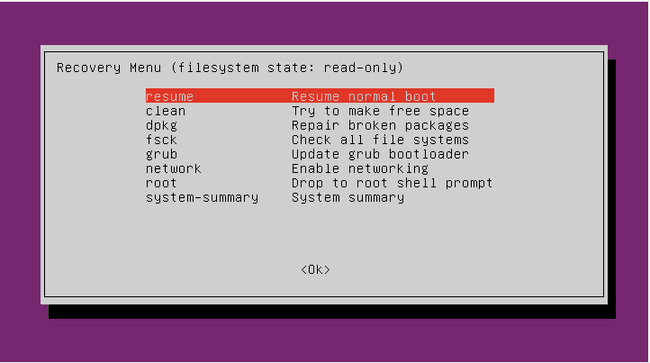
How to Use Recovery Mode Options in Ubuntu
The recovery mode menu has several options that you can use to fix your system. Here is what each option does and when to use it:
- Resume: This option will resume the normal boot process and exit recovery mode. Use this option if you don’t want to make any changes or if you have fixed the problem already.
- Clean: This option will remove any unnecessary or obsolete packages and files from your system. Use this option if you are running low on disk space or if you want to clean up your system.
- Dpkg: This option will try to fix any broken or incomplete package installations or removals. Use this option if you have problems with installing or uninstalling software or if you see errors related to packages.
- Fsck: This option will check and repair any errors in your file system. Use this option if you suspect that your file system is corrupted or damaged or if you see errors related to files or directories.
- Grub: This option will update the GRUB boot loader configuration and detect any other operating systems on your computer. Use this option if you have problems with booting or if you have installed or removed another operating system.
- Network: This option will enable networking on your system. Use this option if you need internet access for updating packages or downloading files.
- Root: This option will drop you into a root shell where you can execute commands as the superuser. Use this option if you need more control over your system or if none of the other options work.
To select an option, use the arrow keys to highlight it and press Enter. Some options may require confirmation or additional input from you. Follow the instructions on the screen to complete the process.
Conclusion
We have learned how to use recovery mode in Ubuntu to fix common problems. Recovery mode is a useful feature that can help you restore your system when it is not working properly. You can access recovery mode by restarting your computer and pressing the F12 key to enter the GRUB menu. You can also choose to edit the GRUB file . From there, you can choose from different options that can help you clean up disk space, update packages, check file system errors, update the boot loader, enable networking, and more.
If you like the content, we would appreciate your support by buying us a coffee. Thank you so much for your visit and support.



