There can be many reasons behind Ubuntu being unable to boot, like, GRUB error, broken package installation, or even a faulty hardware issue. We will be looking at these issues one-by-one and try to solve it.Here are some of the most common Linux Boot issues and their solutions. Bear in mind that these steps are generally for Ubuntu, but could be applied to any Linux system.
Using GRUB Recovery options
GRUB is a default boot loader that comes with most of Linux distributions. It allows you to select multiple operating systems that reside in your hard drive.
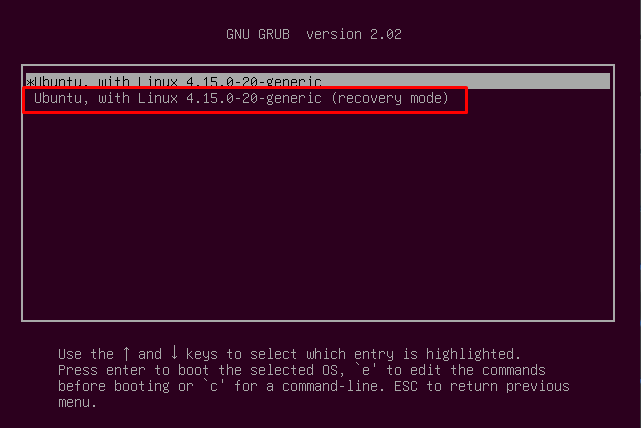
This option is only valid if you can see the GRUB bootloader. In bootloader, look for the option “Advanced options for Ubuntu” and navigate to option recovery mode ( which is not to be confused with ubuntu safe mode ).
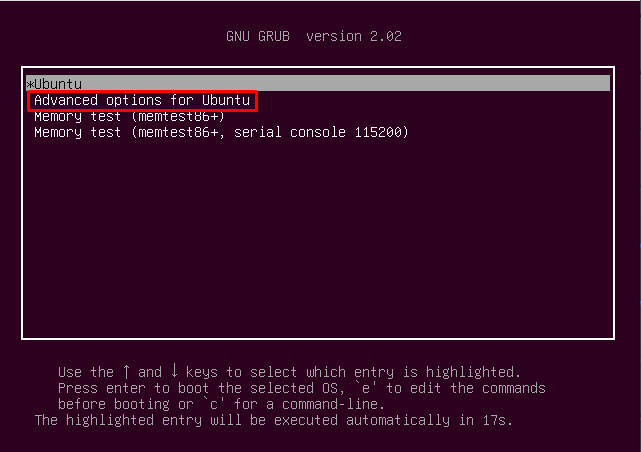 Grub Linux bootloader
Grub Linux bootloader
Read: How to fix “sub process usr/bin/dpkg returned an error code 1″ Error in Ubuntu
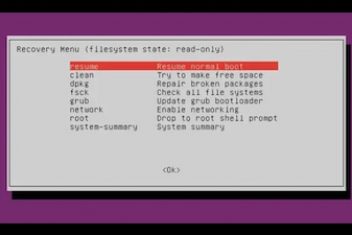
 Uubuntu not booting
Uubuntu not booting
This Recovery mode is very similar to Windows safe mode, it loads only the slimmed down version of Ubuntu. Ubuntu will only load the parts which are absolutely necessary.
Read: How to solve Busybox Initramfs error on Ubuntu
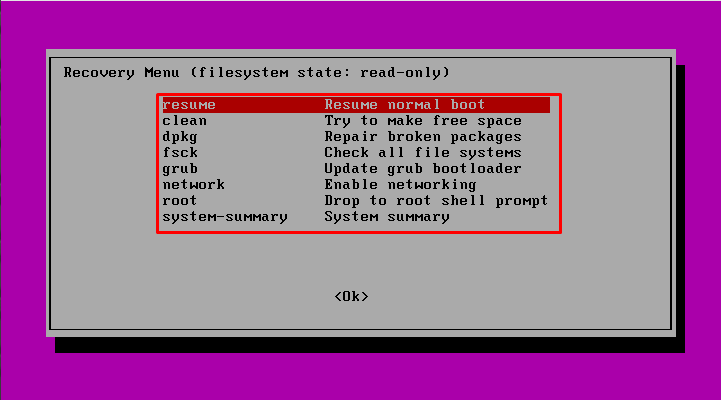
Once Ubuntu starts, you can see many recovery options listed. Here’s a brief discussion:
- resume: it will reboot the system in normal mode again
- clean: this will clean the old downloaded packaged from the cache directory
- dpkg: it will try to recover the broken packages automatically
- fsck: this tool will check the hard drive and try to repair potential problems
- grub: it will update the GRUB if you have some kind of broken GRUB
- network: this will enable networking in safe mode
- root: it will open up a root command prompt (beware that this may cause system-wide issues if you are not careful)
- system-summary: it shows you basic system summary
Once you are done with the settings, select resume and check if the problem got resolved or not.
Read: How to run applications at startup on Ubuntu 18.04?
GRUB Error
When you have a dual boot system and you install Windows (or in some case update it), Windows overwrites the GRUB with its own MBR (Master Boot Record) which unfortunately does not recognize the Linux system, which in turn leads to Ubuntu booting problems.
First, check whether you can access your GRUB or not. To check this, restart the system and press shift while the system is booting. This will open up below screen.
Read: How to Access Recovery Mode in Ubuntu Linux 22.04
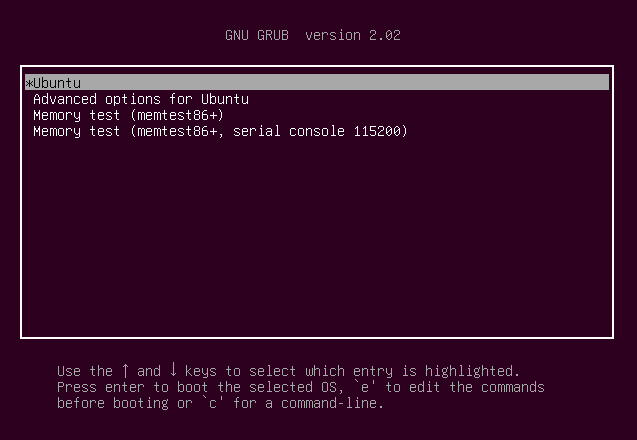
If you cannot see the above screen, then the issue is GRUB itself. We need to repair the Ubuntu Bootloader to be able to boot into the Linux system. If you are using the dual boot system, you will still have access to your Windows system after the repair.
Read: How to restore GRUB Bootloader in Ubuntu
Steps to recover the GRUB
To recover GRUB, you will need a live USB of the Linux system which you are trying to restore, i.e., you will need an Ubuntu 18.04 x64 live USB to recover Ubuntu 18.04. Once you get the USB, boot into it and choose the “Try Ubuntu” option. When it boots into Live USB, follow the steps below (Ubuntu grub repair):
sudo apt-add-repository PPA:yannubuntu/boot-repair
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y boot-repair
Read: How to solve “fsck error on boot: UNEXPECTED INCONSISTENCY”;
Once you install the boot-repair app, you can launch it via below command:
boot-repair [ubuntu boot repair]
When presented, select the Recommended Repair option. There is also one advanced option where you can fine-tune your Linux boot options according to your liking.
Once done, you should now be able to login to your Linux machine.
Reinstall Ubuntu
In the event that Ubuntu still does not boot, the only viable option left is to install Ubuntu once again. In that case, you will again need the live USB.
Read: Must-do Things After Installing Ubuntu 18.04
But before installing Ubuntu, make sure that you have a complete backup of your system as re-installing will remove your old data. You can create a backup while you have live booted. Just make sure that you are backing up data on a partition other than the one you are going to install Ubuntu on.
Replace Hardware
In some cases when you still cannot access your Linux, or rather any of the OS, the problem may be with the hardware itself, but it could be tricky to determine which part of the machine is failing. It is advisable that you seek professional help in that regard.
If you like the content, we would appreciate your support by buying us a coffee. Thank you so much for your visit and support.