In this digital age, we heavily rely on Wi-Fi connectivity for work, entertainment, and communication. But sometimes, you may face frustrating Wi-Fi connection problems on your Mac that disrupt your day-to-day activities.
This comprehensive guide covers the most common Wi-Fi issues on Mac and provides step-by-step troubleshooting tips to get you back online quickly.
Symptoms of Wi-Fi Connectivity Problems on Mac
Here are some of the typical Wi-Fi related problems you may encounter on your Mac:
- Wi-Fi connected but internet not working on Mac – You are connected to the Wi-Fi network but cannot access websites or use internet-based apps.
- Wi-Fi disconnecting frequently – Mac disconnects from wifi every now and then – You keep getting disconnected from the Wi-Fi network randomly.
- Slow Wi-Fi speeds – Websites and downloads are extremely slow over your Wi-Fi connection.
- Other devices connect but Macbook wifi not working – All your other devices can connect to the Wi-Fi fine, but your Mac cannot.
Read: How to properly clean reinstall your MacOS
15 Fixes for Mac Wifi issues
If you are facing any of the above Wi-Fi problems on your Mac, try these troubleshooting steps to resolve the issues:
1. Reboot Your Mac
The simplest fix is to restart your Mac. Shut down your Mac completely and start it up again after a few minutes. Restarting refreshes the network components and connectivity. This can resolve many minor software glitches causing Wi-Fi issues.
2. Restart Your Wireless Router
Like your Mac, restarting the wireless router can also refresh the connections and troubleshoot Wi-Fi problems. Unplug the power cable of your router for 2-3 minutes and then reconnect it to reboot the device. If possible, try changing the location of your router as well. Place it in an open central area for better Wi-Fi coverage.
3. Reset PRAM/NVRAM
PRAM (Parameter RAM) and NVRAM (Non-Volatile RAM) store network settings and other system-level preferences on your Mac. Resetting them clears any corrupt network cache that could be causing Wi-Fi connectivity problems.
To reset PRAM/NVRAM, restart your Mac and hold down Command + Option + P + R keys together until you hear the startup chime again. This will reset the NVRAM and refresh your network components.
4. Check for System Software Updates
Apple keeps releasing software updates to fix bugs, including Wi-Fi-related issues. Go to Apple menu > System Preferences > Software Update and install any available updates, especially for macOS. This could resolve your Wi-Fi problems if they were due to software bugs.
Read: How to fix WiFi not working on Ubuntu
5. Toggle Airplane Mode On/Off
Toggling Airplane mode off and on again restarts your network interfaces and often fixes Wi-Fi problems like not connecting or disconnecting frequently.
Go to System Preferences > Network > Wi-Fi and toggle Airplane mode on. Wait for 15-20 seconds and turn it off. Then try connecting to the Wi-Fi again.
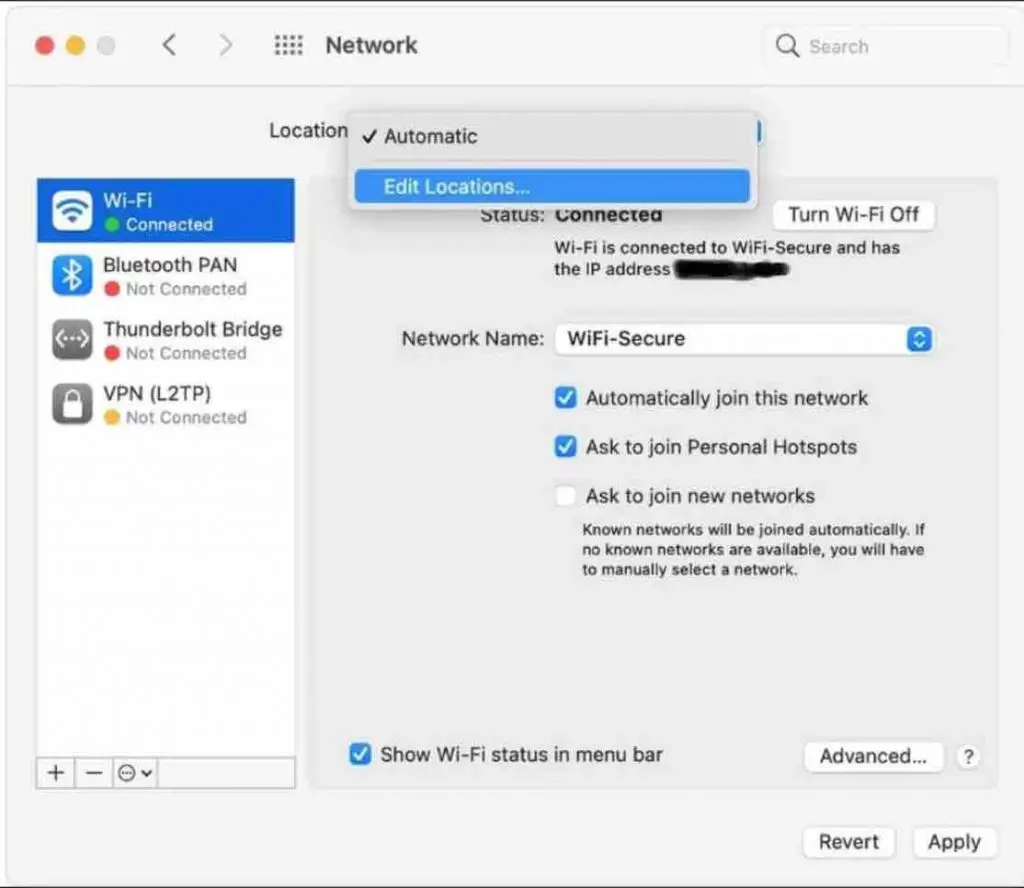
6. Delete and Recreate the Network Location
If your existing network location has become corrupted, deleting it and creating a new one can resolve Wi-Fi issues.
Go to System Preferences > Network > Location. Click the Edit Locations icon, press the “-” button to remove your problematic Wi-Fi connection. Then click “+” to add it again with the correct settings.
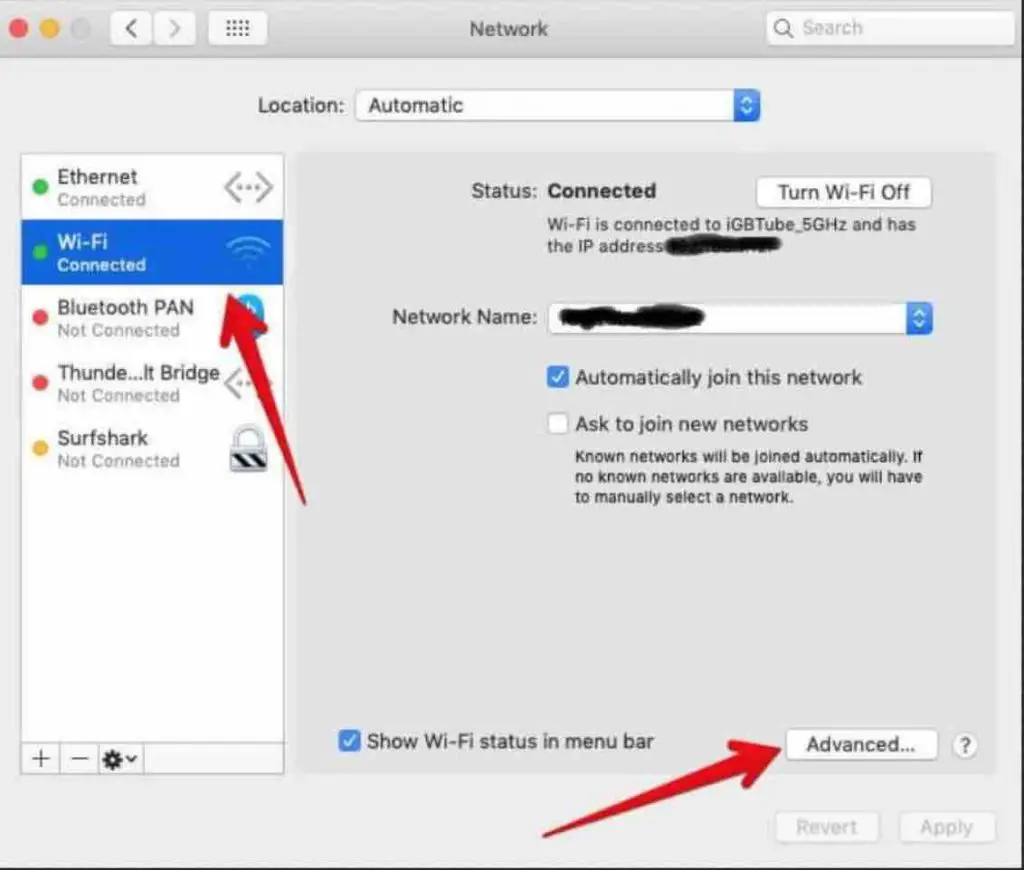
7. Renew DHCP Lease
DHCP automatically assigns an IP address to your Mac from the router so that it can communicate over the network. Sometimes renewing the DHCP lease fixes Wi-Fi connectivity problems.
Go to System Preferences > Network > Wi-Fi > Advanced > TCP/IP. Click “Renew DHCP Lease” and see if this resolves your issues.
8. Reset SMC and PRAM/NVRAM
For stubborn Wi-Fi problems, reset both SMC (System Management Controller) and PRAM. This clears all network settings and reinitializes the network components.
To reset SMC, shut down your Mac and press Shift + Control + Option + Power button for 10 seconds. For PRAM reset, on restart press Command + Option + P + R keys until you hear the startup chime again.
9. Update Router Firmware
Outdated router firmware can also cause Wi-Fi connectivity problems. Log into your wireless router’s admin console and check if there is a firmware update available. Install the latest firmware to resolve any bugs.
10. Fix Mac Wi-Fi Interference from Nearby Networks
Wi-Fi connections can suffer interference from competing signals in dense areas like apartment buildings. Overlapping wireless networks create radio congestion that disrupts connectivity.
To resolve Wi-Fi conflicts on Mac:
- Give your network a unique SSID name to differentiate it.
- Set your router to “Auto” channel selection so it chooses the least crowded frequency.
- Alternatively, log into the router config and manually change the channel based on an analysis of nearby networks.
- Use Wireless Diagnostics on Mac to view signal strength on each channel and pick one with minimal interference.
Taking steps to reduce Wi-Fi interference by selecting optimal channels and SSID names can significantly improve connection quality. congested wireless environments require proactive optimization for reliable bandwidth on Mac systems.
Read: How to remove unused WiFi networks in Windows 10
11. Switch to 5GHz Wi-Fi Band
The 5GHz Wi-Fi band offers better performance than the commonly used 2.4GHz band. If your router is dual-band, change its settings to connect your Mac to the less crowded 5GHz network for faster and more reliable connectivity.
12. Troubleshoot with Network Diagnostics
macOS includes advanced networking diagnostics to detect Wi-Fi problems. Here are the two utilities you can use:
a. Network Diagnostics
This tool automatically checks for common Wi-Fi issues and suggests fixes. To use it:
- Go to Apple menu > System Preferences > Network > Assist me
- Select your Wi-Fi connection and click Diagnostics
- Follow the onscreen instructions
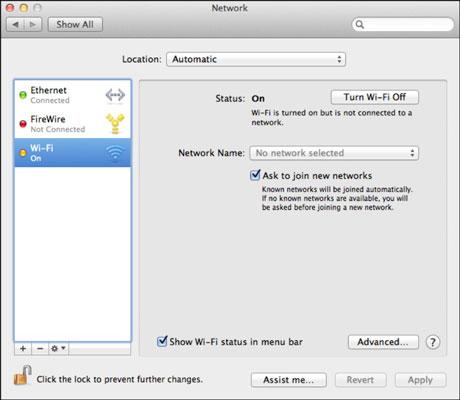
Network Diagnostics checks for these problems:
- DNS server not responding
- Problems with IP address and DHCP
- Captive portal blocking access
- Firewall or filters blocking access
- Server not responding
- No internet connection detected
Based on the issue, it will suggest fixes like renewing the DHCP lease, verifying DNS settings, checking for firewall restrictions etc.
Read: How to Quit All Your Apps at the Same Time on Your Mac
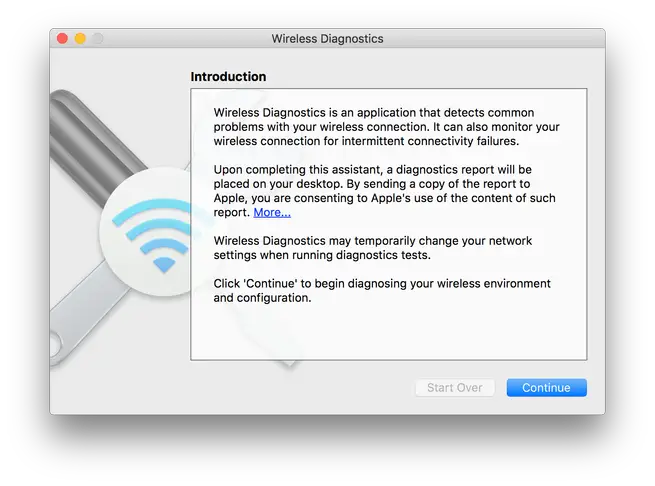
b. Wireless Diagnostics
For advanced monitoring and troubleshooting, use the Wireless Diagnostics utility:
- Hold the Option key and click the Wi-Fi icon in the menu bar
- Select “Open Wireless Diagnostics”
- Click Continue and follow prompts
Read: The Ultimate iPhone Troubleshooting Guide: 20 Common Problems and Solutions
This will generate a detailed report about your Wi-Fi connection. It checks for:
- Connection errors
- Signal strength issues
- Router configuration problems
- Interference from other networks
- Hardware faults
The scan results can help identify what is causing the Wi-Fi problems on your Mac. You can then take steps like changing the router channel, adjusting antenna orientation, updating firmware or drivers etc.
Read: Windows 10 doesn’t remember your WIFI password? Here is how to fix it.
13 Disconnecting Bluetooth and Removing USB Devices
In certain instances, Bluetooth, USB, and other wireless devices emit signals that can potentially interfere with your WiFi connectivity. To address this concern effectively, consider removing USB devices connected to your Mac individually to assess if the issue is resolved.
For disconnecting Bluetooth, adhere to the following steps:
- Open the Apple menu
- Navigate to System Preferences
- Select Bluetooth
- Toggle the Bluetooth switch to the ‘off’ position
Read: How to Fix `dyld: Library not loaded: icu4c` Errors on macOS After Homebrew Operations
14 . Change DNS to Fix Internet Connectivity on Mac
The Domain Name System (DNS) converts website names to IP addresses that computers can understand. Sometimes the DNS provided by an internet service provider fails, causing connectivity issues. In these cases, switching to a public DNS like Google’s free option can resolve internet problems on a Mac.
To change the DNS settings:
- Hit the Wi-Fi icon in the top menu bar
- Select “Advanced”
- Click on DNS
- Add Google’s DNS address (8.8.8.8) by clicking the plus icon
- Click “OK” to save changes
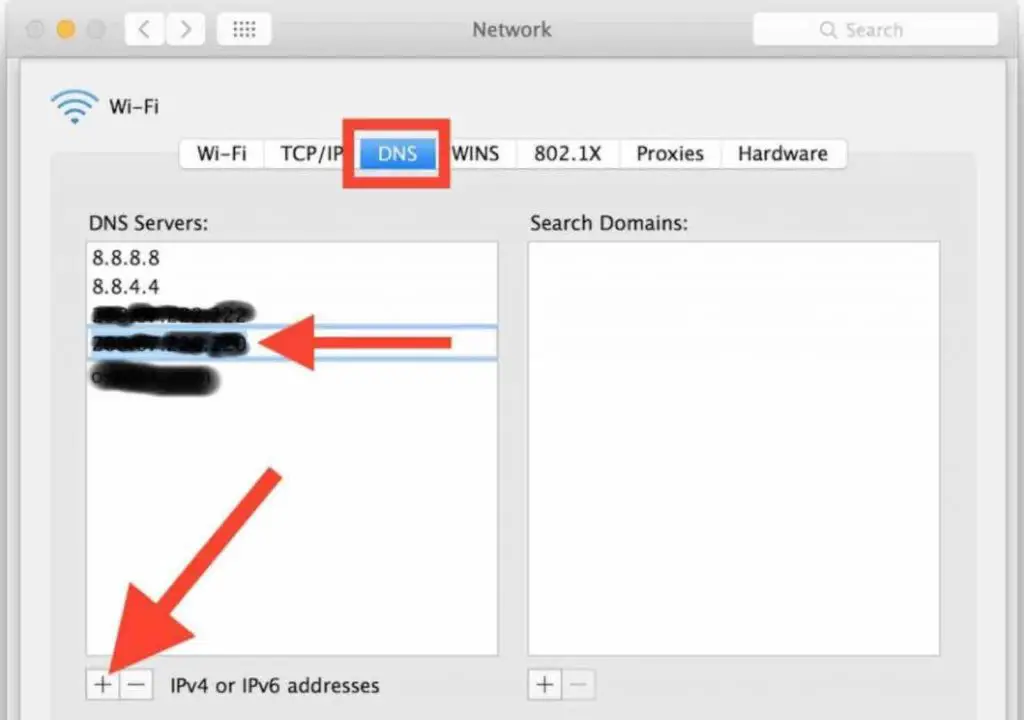
After updating the DNS configuration, try accessing websites and internet services again. Using reliable public DNS servers often fixes connection problems caused by faulty ISP DNS. Simply updating the address Mac uses for domain name resolution can get your internet working again.
15. Reset Network Settings to Fix Mac Wi-Fi Connectivity
Sometimes corrupted network settings cause persistent Wi-Fi problems on Mac. Resetting the configuration often resolves connectivity issues after sleep or other wifi headaches.
Before resetting, backup key network preferences files:
1. Navigate to ~/Library/Preferences/SystemConfiguration/
2. Save the following files to a separate folder:
- – com.apple.airport.preferences.plist
- – com.apple.network.identification.plist
- – com.apple.wifi.message-tracer.plist
- – NetworkInterfaces.plist
- – preferences.plist
Next, restart your Mac and test the Wi-Fi. If problems persist, create a new network location:
- – Open System Preferences > Network > Wi-Fi
- – Click the locations menu and choose Edit Locations
- – Click + to add a location and give it a unique name
- – Click Done
Then configure the new location:
- – Go to Advanced and renew the DHCP lease
- – In DNS, add 8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4 (Google DNS)
- – Set MTU to Custom 1453
- – Click OK and Apply
This Wi-Fi reset process often resolves issues like dropping connections after sleep. Backing up and creating a fresh configuration can get Mac networking working again.
Read: How to find out who is using your wifi
When to Call Your ISP?
If none of the above DIY troubleshooting tips fix your Mac’s Wi-Fi problems, then the issue could be with your ISP’s equipment. Contact your Internet Service Provider if you face problems like:
- Total loss of internet (and not just Wi-Fi)
- Connection issues with the ISP provided router/modem
- Internet is not working on Mac
- Other ISP subscribers in your area also face problems
ISP support can diagnose and resolve problems like area outages, faulty modems, line issues etc. They may send a technician for repairs if required.
Preventing Future WiFi Not Working on Mac Problems
Along with troubleshooting existing Wi-Fi problems, also take these measures to avoid issues in the future:
- Position your router centrally in open space for best coverage
- Keep the router firmware updated
- Set unique router SSID and passwords
- Use 5GHz band for less interference
- Limit the number of connected devices
- Scan for channel conflicts and switch channels
- Maintain backups of router settings
- Buy a newer and better router if needed
Following these tips will help minimize Wi-Fi headaches and keep your Mac seamlessly connected for work and entertainment. Contact Apple support if problems persist even after trying all these steps.
If you like the content, we would appreciate your support by buying us a coffee. Thank you so much for your visit and support.